Hemppocampus Pattern
I'm going to share some information about Hemp plants and how they are used to improve neuroplasticity and the hippocampus, and about how this plant stalk is used for fiber to create useful items
For the third edition of the Neuronknit Series, I'm going to share some information about Hemp plants and how they are used to improve neuroplasticity and the hippocampus, and about how this plant stalk is used for fiber to create useful items for everyday use such as clothing and household items. I have created a knitting pattern with handspun hemp yarn and cashmere cotton to make some really beautiful hand or face towels and dinner napkins.
Why focus on the Hippocampus?
This series is about using knitting as a tool for recovery after a traumatic brain injury. One of the many symptoms after an injury is dizziness (learning how to balance again) to much severe symptoms that needs re-learning.
What is plasticity in the hippocampus?
Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus assists with consolidation and storage of long-lasting memories.
Main Function
Hippocampus is a complex brain structure embedded deep into temporal lobe. It has a major role in learning and memory. It is a plastic and vulnerable structure that gets damaged by a variety of stimuli. Studies have shown that it also gets affected in a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Main Target
Memories are not stored in the hippocampus for the long term. Instead, it is believed that the hippocampus acts as something of a shipping center, taking in information, registering it, and temporarily storing it before shipping it off to be filed and stored in long-term memory.
***
About the Hemp plant
The hemp plant is a stout, aromatic, erect annual herb. The slender canelike stalks are hollow except at the tip and base. The leaves are compound with palmate shape, and the flowers are small and greenish yellow. Seed-producing flowers form elongate spikelike clusters growing on the pistillate, or female, plants. Pollen-producing flowers form many-branched clusters on staminate, or male, plants.
hemp, (Cannabis sativa), also called industrial hemp, plant of the family Cannabaceae cultivated for its bast fibre or its edible seeds. Hemp is sometimes confused with the cannabis plants that serve as sources of the drug marijuana and the drug preparation hashish. Although all three products—hemp, marijuana, and hashish—contain tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), a compound that produces psychoactive effects in humans, the variety of cannabis cultivated for hemp has only small amounts of THC relative to that grown for the production of marijuana or hashish.
hemp and CBD
In general, one hemp plant yields about one pound of CBD tincture. That said, the exact yield of CBD extract per plant depends on the percentage of CBD per plant. It varies by strain, but it is typically 15%-22%. Another factor that affects how much a plant can actually produce is the quality of the plant.
***
In a study reported by Journal of Translational Medicine
Results Show
CBD produced a dose-dependent polarization of activation along the rostral-caudal axis of the brain. The olfactory bulb and prefrontal cortex showed an increase in positive BOLD whereas the brainstem and cerebellum showed a decrease in BOLD signal. This negative BOLD affected many areas connected to the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS). The ARAS was decoupled to much of the brain but was hyperconnected to the olfactory system and prefrontal cortex.
Conclusion
The CBD-induced decrease in ARAS activity is consistent with an emerging literature suggesting that CBD reduces autonomic arousal under conditions of emotional and physical stress.
Hemp Fibers
Fiber Production
Hemp is a bast fiber plant like jute. Hemp fiber consists of two types: bast and hurd. Certain varieties of hemp are grown for fiber content. Fiber is harvested from the stalks of hemp fiber varieties and consists of long bast fibers (2–25 mm) and shorter hurd fibers. These fibers are separated from the bark through a process called “retting.” The fibers are then spun together to produce a continuous thread that can be woven into a fabric.
Hemp plants will mature for fiber production in 60-90 days and for grain in 90-120 days. Hemp thrives in sunny summer days, (greater than 14 hours), but requires shorter (approximately 12-hour days) to produce mature flowers or seed. Summer day high temperatures from 80 to 90 degrees Fahrenheit are optimal for healthy hemp growth. Nighttime temperatures should be about 10 to 15 degrees lower.
Is hemp really better than cotton?
The hemp fabric lasts longer and doesn't wear out as quickly as cotton does. Hemp has three times more tensile and flexible strength than cotton, holding its shape time and again and becomes softer after each wear and wash. Hemp is a more premium fabric.
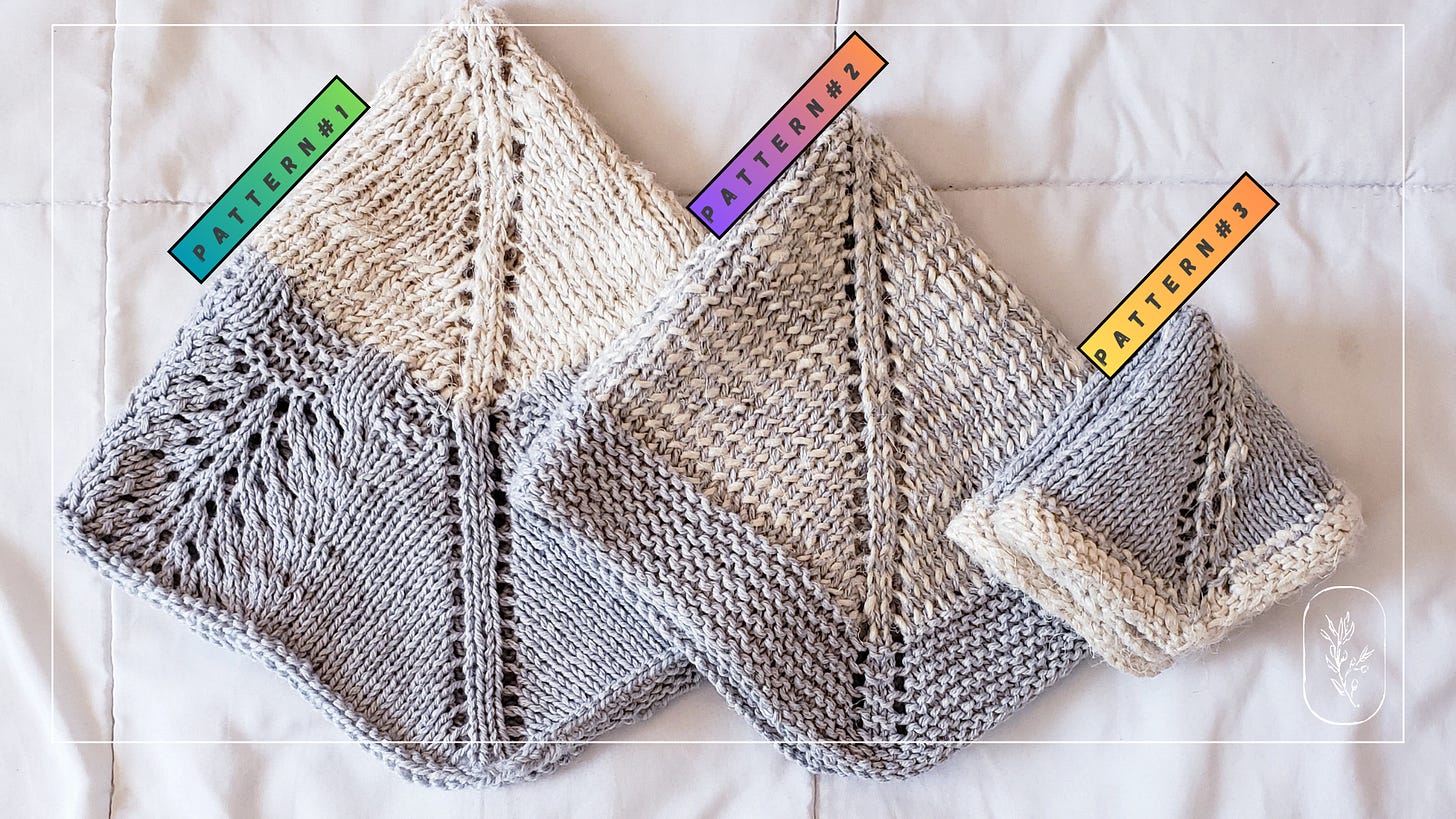
About the Hemppocampus Knit Pattern
The real quiet luxury!
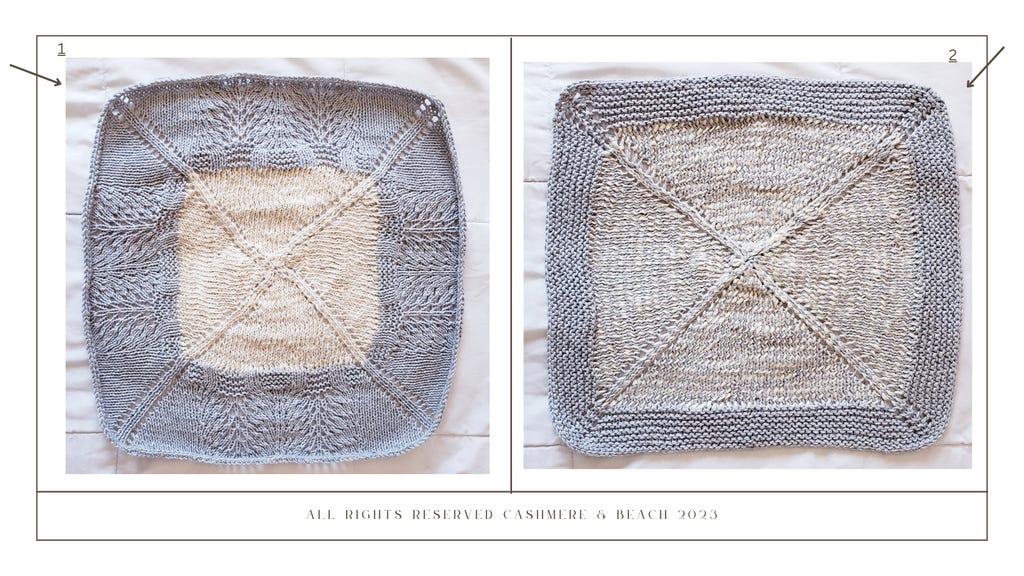
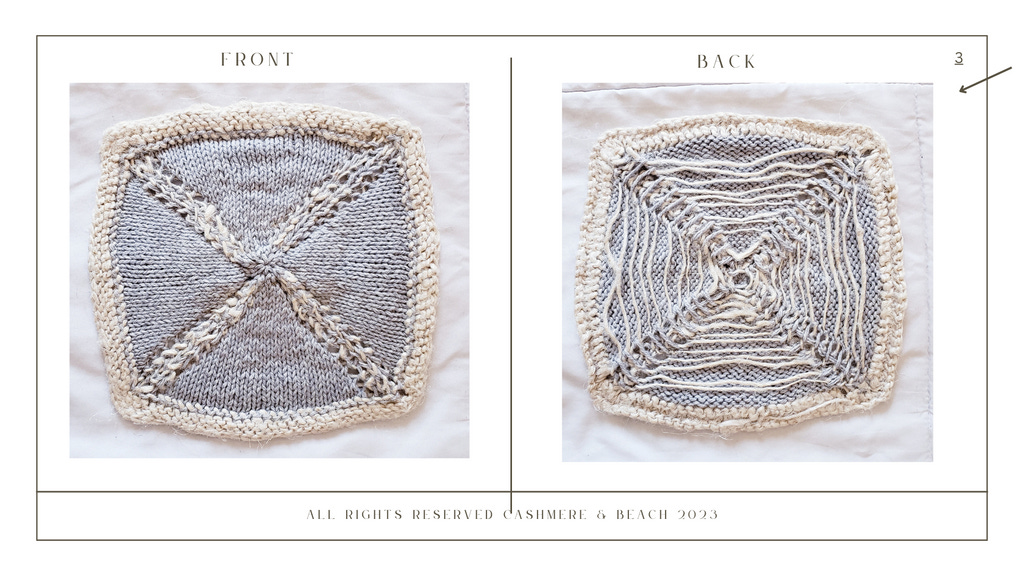
The Hemppocampus set are there beautiful hemp and cashmere square patterns in different sizes that can be used as hand and face towels or dinner and picnic napkins. The different sizes as well as the different patterns can be used for practical needs while being beautiful and luxurious.
The square are knitted from center out and can be as big or small as you want.
The designs are for a reason.
Pattern1. face towel one side cashmere with other size hemp to exfoliate.
Pattern 2. is stripped and evenly for ultimate multi use.
Pattern 3. is a table napkin or a lap napkin
Knitting for Neuroplasticity
A significant contributor to neuroplasticity is adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN), the process by which new neurons are generated from adult neural stem cells.
The practice of the knit stitch in coordination with increase stitches by numbers that transform a 1 dimensional string into a 3 dimensional object is the success of strengthen neurons.
Materials
DPN - US7
Circular knitting needles US7
5 ounce hemp fiber
2 Rowan cotton/cashmere yarn
Drop spindle
4 stitch markers
Abbreviations
BO: bind off
BOR: beginning of round
DPNs: double pointed needles
KFB: Knit front to back
K: knit
K2TOG: knit two together
M: marker
P: purl
PM: place marker
RNDS: Rounds
SM: slip marker
SSK: slip, slip, knit
ST(S): stitch(es)
YO: yarn over
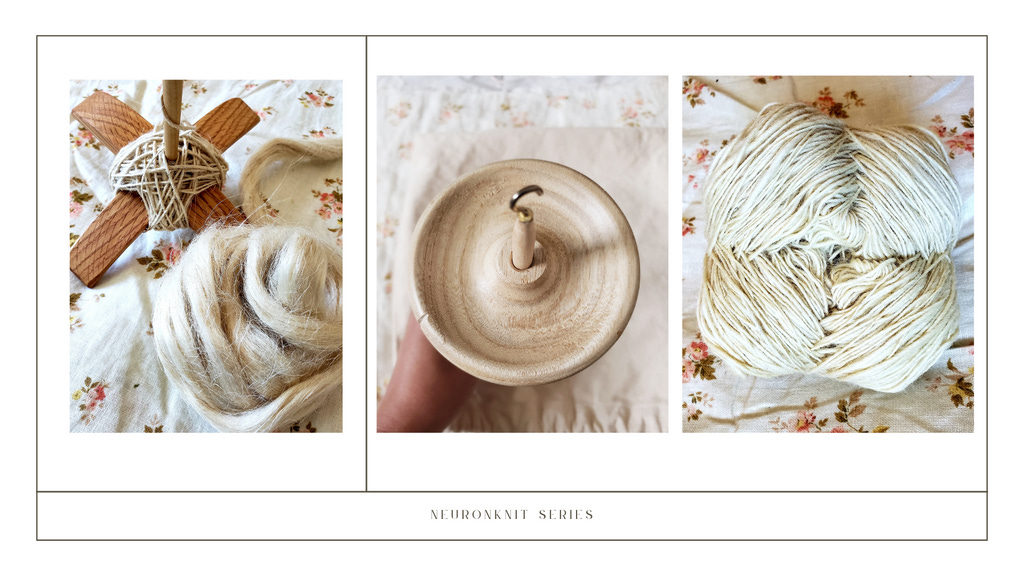
Spinning
Intro to yarn spinning
For the purpose of this pattern, I will focus on spindle spinning instead of spinning with a machine. There are many types of spindles and I will focus on the "top whorl" spindle. I used qiviut fiber for this project, however you can use any wool, plant or synthetic fiber you want
Step 1: Pre-draft
Break off a piece of roving about a foot long, and pull gently about 2 to 4 inches at a time to loosen the fiber to the end. Keep gently stretching out the roving until it is at least twice as long as the original length
Step 2 Pre-draft
Using a piece of scrap yarn tie a piece about a foot long to the shaft of your spindle, any old knot will do. Bring the leader around the edge of the whorl (many spindles have a handy notch in the edge for this purpose) and under the hook at the top of the spindle shaft.
Before introducing your fiber into the equation, you will give your spindle a (clockwise) spin by twirling the shaft below the whorl and letting it hang from the leader. The spindle keeps going for some time before the twist in the yarn fights back and slows it down.
Step 3: How to manage pre-draft yarn for spinning
Wrap your pre-drafted roving around your wrist. As you spin, you'll unwind the roving from your wrist. or your may throw over your shoulder to keep out of your way.
Step 4: Spinning
give your spindle a good clockwise spin, and let it hang, keeping your hand pinching leader (that has the waste yarn attached) and fiber together. You should notice the fiber twisting onto the leader. Let the leader build up a good amount of twist, then attach the pre-draft roving and allow the twist to twist into the roving. Repeat this process a couple of times.
Step 5: Wind on
Your newly spun yarn will eventually get too long. So you will unhook the yarn and wind all but 10' or so around the shaft of your spindle, then bring it around the whorl and into the hook again. Repeat this process until you have spin all of your roving.
Knitting Instructions
Cast On/#1 pattern
Cast-on 8 stitches using the circle cast on method.
Round 1: Knit
Round 2: YO all STS (16 STS) place BOR marker
Round 3: K
Round 4: k1, YO , k 2, yo, place marker, k 2, place marker yo, k 2, yo, place marker, k1
Rounds 5 K
continue to increase row every other round until you reach 34 sts on each side. ( 136 sts total)
Boarder
Note: you will continue to increase every other round.
Round 1: K1, yo, place marker, k34, place marker, yo, k1, slp m, repeat 3 more times to complete round.
Round 2: slp BOR m, k2 slip m, p3, k3, p5, k3, p6, k3, p5, k3, p3 slp m, k2 slp m, continue 3 more times to complete the round.
repeat round 1 and 2 three more times.
Next round, repeat round 1 only.
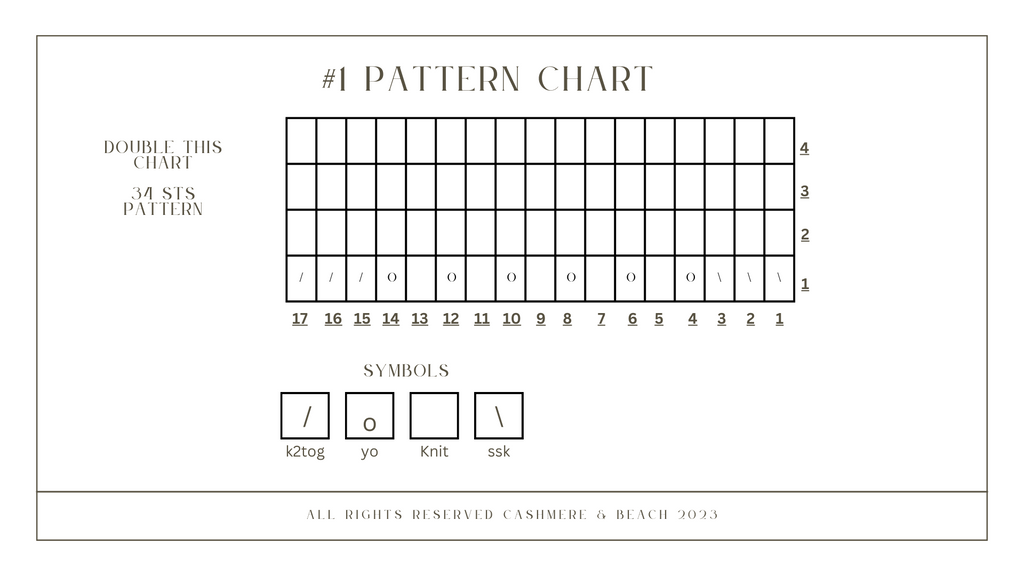
Chart
Follow the chart while also continuing the increases on every other row.
Repeat the chart 4 times.
Bind off
p to EOR
Standard bind- off
Cast On/#2 pattern
Pattern #2 is knitted the same, the only difference is changing yarn each round
Cast-on 8 stitches using the circle cast on method.
Round 1: Knit
Round 2: YO all STS (16 STS) place BOR marker
Round 3: K
Round 4: k1, YO , k 2, yo, place marker, k 2, place marker yo, k 2, yo, place marker, k1
Rounds 5 K
continue to increase row every other round until you reach 44 sts on each side. ( 176 sts total)
Boarder
Note: you will continue to increase every other round.
Round 1: k
Round 2: p
continue round 1 and 2 six more times
Bind off
Standard bind off
Cast On/#3 pattern
Pattern #3 is knitted the same, the only difference is changing (hemp) yarn at the increase stitch.
cast-on 8 stitches using the circle cast on method.
Round 1: Knit
Round 2: YO all STS (16 STS) place BOR marker
Round 3: K
Round 4: k1, YO , k 2, yo, place marker, k 2, place marker yo, k 2, yo, place marker, k1
Rounds 5 K
continue to increase row every other round until you reach 26 sts on each side. ( 104 sts total)
I cord Bind off
Knit 1 round in hemp yard before you start the bindoff.
R1: Start KFB, by placing STS onto the woring needle. Repeat 2 more times for a total of 3 additional STS.
iR2: K2, K2TOG through the back loop, place 3 knitted STS back onto the working needle
Repeat R1-2 until bindoff is complete